在上一个教程中,我们学习了如何在 C 中使用if语句。在本指南中,我们将学习如何使用 C 语句中的if else,嵌套if else和else语句。
C if-else语句
if else语句的语法:
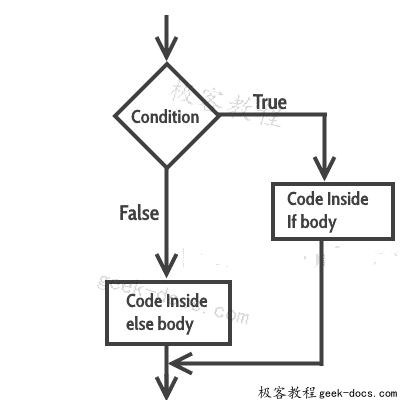
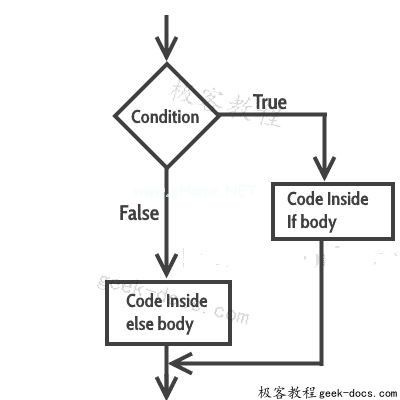
如果条件返回true,则执行if正文内的语句,并跳过else正文内的语句。
如果条件返回false,则跳过if正文中的语句,并执行else中的语句。
if(condition) { // Statements inside body of if}else { //Statements inside body of else}if-else语句的流程图
if-else语句的示例
在此程序中,要求用户输入年龄,并根据输入,if..else语句检查输入的年龄是否大于或等于 18。如果满足此条件,则显示消息“您有资格投票”,但是,如果条件不符合,则显示不同的消息“您没有资格投票”。
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ int age; printf("Enter your age:"); scanf("%d",&age); if(age >=18) { /* This statement will only execute if the * above condition (age>=18) returns true */ printf("You are eligible for voting"); } else { /* This statement will only execute if the * condition specified in the "if" returns false. */ printf("You are not eligible for voting"); } return 0;}输出:
Enter your age:14You are not eligible for voting
注意:如果只有一个语句出现在if或else正文中,那么你不需要使用大括号(括号)。例如,上面的程序可以像这样重写:
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ int age; printf("Enter your age:"); scanf("%d",&age); if(age >=18) printf("You are eligible for voting"); else printf("You are not eligible for voting"); return 0;}C 嵌套if-else语句
当if else语句出现在另一个if或else的正文内时,则称为嵌套if-else。
嵌套if语句的语法:
if(condition) { //Nested if else inside the body of "if" if(condition2) { //Statements inside the body of nested "if" } else { //Statements inside the body of nested "else" }}else { //Statements inside the body of "else"}嵌套if-else的示例
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ int var1, var2; printf("Input the value of var1:"); scanf("%d", &var1); printf("Input the value of var2:"); scanf("%d",&var2); if (var1 != var2) { printf("var1 is not equal to var2\n"); //Nested if else if (var1 > var2) { printf("var1 is greater than var2\n"); } else { printf("var2 is greater than var1\n"); } } else { printf("var1 is equal to var2\n"); } return 0;}输出:
Input the value of var1:12Input the value of var2:21var1 is not equal to var2var2 is greater than var1
C – else..if语句
当需要检查程序中的多个条件时,else..if语句很有用,可以使用else..if语句避免嵌套if-else块。
else..if语法的语法:
if (condition1) { //These statements would execute if the condition1 is true}else if(condition2) { //These statements would execute if the condition2 is true}else if (condition3) { //These statements would execute if the condition3 is true}..else { //These statements would execute if all the conditions return false.}else..if语句的示例
让我们在讨论嵌套的if..else时采用我们在上面看到的相同示例。我们将使用else..if语句重写相同的程序。
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ int var1, var2; printf("Input the value of var1:"); scanf("%d", &var1); printf("Input the value of var2:"); scanf("%d",&var2); if (var1 !=var2) { printf("var1 is not equal to var2\n"); } else if (var1 > var2) { printf("var1 is greater than var2\n"); } else if (var2 > var1) { printf("var2 is greater than var1\n"); } else { printf("var1 is equal to var2\n"); } return 0;}输出:
Input the value of var1:12Input the value of var2:21var1 is not equal to var2
正如您所看到的那样,只执行if正文中的语句。这是因为在该语句中,只要满足条件,就会执行该块内的语句,并忽略其余的块。
重要事项:
- else和else..if是可选语句,只有if语句的程序运行正常。否则,如果没有if,则无法使用。if else..if块中可以有任意数量的else..if语句。如果没有满足任何条件,则执行else块中的语句。就像关系运算符一样,我们也可以使用逻辑运算符,如 AND(&&),OR(||)和 NOT(!)。