C语言中while(1)和while(0)的区别
在大多数计算机编程语言中,while循环是一种控制流语句,允许根据给定的布尔条件重复执行代码。布尔条件为真或假。
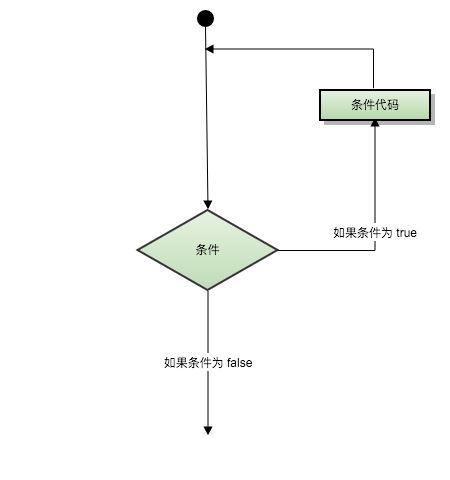
while(1)
它是一个无限循环,将一直运行到显式发出break语句为止。有趣的是,不是while(1)而是任何非零的整数都会产生与while(1)类似的效果。因此,while(1), while(2)或while(-255), all将只给出无限循环。
我们将条件写在括号()中。条件可以解析为真或假。0代表假,其他值都是真。
所以逻辑:
While (true) == While (1)== While(任何表示true的值);
而(false) = =, (0);
while(1) or while(any non-zero integer){ // loop runs infinitely}在Client-Server程序中可以简单地使用while(1)。在程序中,服务器运行在无限的while循环中,以接收来自客户端发送的数据包。
但实际上,在现实世界中使用while(1)是不可取的,因为它会增加CPU的使用,并且还会阻塞代码i.e,直到程序手动关闭。而(1)可以用于条件总是为真的地方。
// C program to illustrate while(1)#include <stdio.h>int main(){ int i = 0; while (1) { printf("%d\n", ++i); if (i == 5) break; // Used to come // out of loop } return 0;}#include <iostream>using namespace std; int main(){ int i = 0; while (1) { cout << ++i << "\n"; if (i == 5) // Used to come // out of loop break; } return 0;}输出:
12345
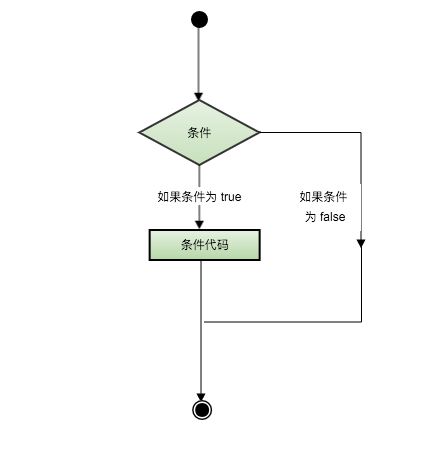
while(0)
它与while(1)相反。这意味着condition将永远为假,因此while中的代码永远不会被执行。
while(0){ // loop does not run}// C program to illustrate while(0)#include<stdio.h>int main(){ int i = 0, flag=0; while ( 0 ) { // This line will never get executed printf( "%d\n", ++i ); flag++; if (i == 5) break; } if (flag==0) printf ("Didn't execute the loop!"); return 0;}#include <iostream>using namespace std; int main() { int i = 0, flag=0; while ( 0 ) { // This line will never get executed cout << ++i << "\n"; flag++; if (i == 5) break; } if (flag==0) cout << "Didn't execute the loop!"; return 0;}输出
Didn't execute the loop!