循环用于重复执行语句块,直到满足特定条件。例如,当您显示从 1 到 100 的数字时,您可能希望将变量的值设置为 1 并将其显示 100 次,在每次循环迭代时将其值增加 1。
在 C++ 中,我们有三种类型的基本循环:for,while和do-while 。在本教程中,我们将学习如何在 C++ 中使用for 循环。
for循环的语法
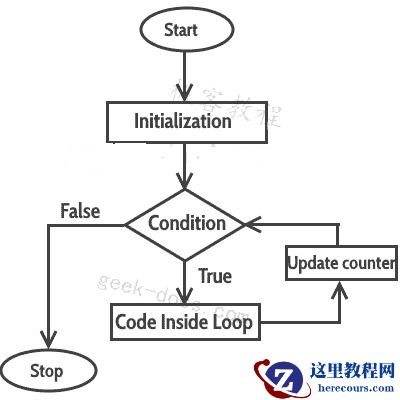
for(initialization; condition ; increment/decrement){ C++ statement(s);}for循环的执行流程
当程序执行时,解释器总是跟踪将要执行的语句。我们将其称为控制流程或程序的执行流程。
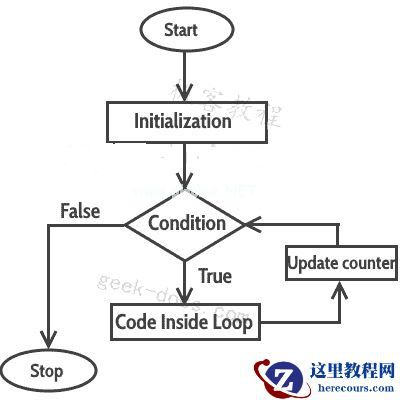
第一步:在for循环中,初始化只发生一次,这意味着for循环的初始化部分只执行一次。
第二步: for循环中的条件在每次循环迭代时进行计算,如果条件为真,则for循环体内的语句将被执行。一旦条件返回false,for循环中的语句就不会执行,并且控制被转移到程序中for循环后的下一个语句。
第三步:每次执行for循环体后,for循环的递增/递减部分更新循环计数器。
第四步:第三步后,控制跳转到第二步,重新求值条件。
从第二到第四的步骤重复,直到循环条件返回false。
C++ 中的简单for循环示例
这里,在循环初始化部分中,将变量i的值设置为 1,条件是i <= 6,并且在每次循环迭代中,i的值递增 1。
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ for(int i=1; i<=6; i++){ /* This statement would be executed * repeatedly until the condition * i<=6 returns false. */ cout<<"Value of variable i is: "<<i<<endl; } return 0;}输出:
Value of variable i is: 1Value of variable i is: 2Value of variable i is: 3Value of variable i is: 4Value of variable i is: 5Value of variable i is: 6
C++ 中的无限循环
当循环重复执行并且永不停止时,循环被认为是无限的。这通常是错误的。当你在for循环中设置条件时它永远不会返回false,它就会变成无限循环。
例如:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ for(int i=1; i>=1; i++){ cout<<"Value of variable i is: "<<i<<endl; } return 0;}这是一个无限循环,因为我们递增i的值,因此它总是满足条件i <= 1,条件永远不会返回false。
这是无限for循环的另一个例子:
// infinite loopfor ( ; ; ) { // statement(s)}示例:使用for循环显示数组元素
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){ int arr[]={21,9,56,99, 202}; /* We have set the value of variable i * to 0 as the array index starts with 0 * which means the first element of array * starts with zero index. */ for(int i=0; i<5; i++){ cout<<arr[i]<<endl; } return 0;}输出:
2195699202