Java Scanner 类
Scanner是java.util包中的一个类,用于获取原始类型的输入,如int、double等和字符串。它是在Java程序中读取输入的最简单的方法,不过如果你想在时间有限的情况下(如竞争性编程)使用一种输入方法,则不是很有效。
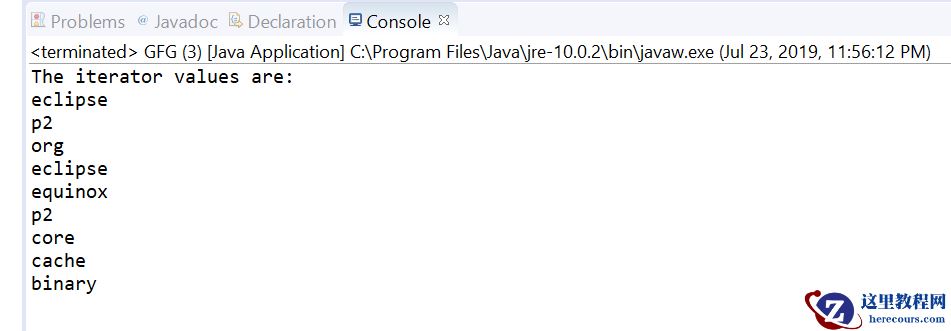
为了创建一个Scanner类的对象,我们通常会传递预定义的对象System.in,它代表标准输入流。如果我们想从一个文件中读取输入,我们可以传递一个File类的对象。要读取某个数据类型XYZ的数值,要使用的函数是 nextXYZ()。例如,要读取一个短类型的值,我们可以使用 nextShort()要读取字符串,我们使用nextLine()。读取单个字符,我们使用next().charAt(0)。 next()函数将输入的下一个标记/字作为字符串返回,charAt(0)函数返回该字符串的第一个字符。扫描器类读取整行并将该行划分为标记。标记是对Java编译器有一定意义的小元素。例如,假设有一个输入字符串。How are you 在这种情况下,扫描器对象将读取整行,并将该字符串划分为标记。”How”、”are “和 “you”。然后,该对象对每个标记进行迭代,并使用其不同的方法读取每个标记。让我们看一下读取各种数据类型的代码片断。
// Java program to read data of various types using Scanner class.import java.util.Scanner;public class ScannerDemo1{ public static void main(String[] args) { // Declare the object and initialize with // predefined standard input object Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // String input String name = sc.nextLine(); // Character input char gender = sc.next().charAt(0); // Numerical data input // byte, short and float can be read // using similar-named functions. int age = sc.nextInt(); long mobileNo = sc.nextLong(); double cgpa = sc.nextDouble(); // Print the values to check if the input was correctly obtained. System.out.println("Name: "+name); System.out.println("Gender: "+gender); System.out.println("Age: "+age); System.out.println("Mobile Number: "+mobileNo); System.out.println("CGPA: "+cgpa); }}
输入:
GeekF4098765432109.9
输出:
Name: GeekGender: FAge: 40Mobile Number: 9876543210CGPA: 9.9
有时,我们必须检查我们读取的下一个值是否属于某种类型,或者输入是否已经结束(遇到了EOF标记)。
然后,我们在hasNextXYZ()函数的帮助下检查扫描仪的输入是否是我们想要的类型,其中XYZ是我们感兴趣的类型。如果扫描器有该类型的标记,该函数返回真,否则返回假。例如,在下面的代码中,我们使用了hasNextInt()。要检查一个字符串,我们使用hasNextLine()。同样地,要检查单个字符,我们使用hasNext().charAt(0)。
让我们看一下从控制台读取一些数字并打印其平均值的代码片段。
// Java program to read some values using Scanner// class and print their mean.import java.util.Scanner; public class ScannerDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Declare an object and initialize with // predefined standard input object Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // Initialize sum and count of input elements int sum = 0, count = 0; // Check if an int value is available while (sc.hasNextInt()) { // Read an int value int num = sc.nextInt(); sum += num; count++; } if (count > 0) { int mean = sum / count; System.out.println("Mean: " + mean); } else { System.out.println( "No integers were input. Mean cannot be calculated."); } }}输入 。
1 2 3 4 5 a
输出
Mean: 397