Spring Boot PostgreSQL 教程展示了如何在 Spring Boot 应用中使用 PostgreSQL 数据库。
Spring 是用于创建企业应用的流行 Java 应用框架。 Spring Boot 是 Spring 框架的演进,可帮助您轻松创建独立的,生产级的基于 Spring 的应用。
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL 是一个功能强大的开源对象关系数据库系统。 它是一个多用户数据库管理系统。 它可以在包括 Linux,FreeBSD,Solaris,Microsoft Windows 和 Mac OS X 在内的多个平台上运行。PostgreSQL 由 PostgreSQL 全球开发小组开发。
PostgreSQL 设置
我们将展示如何在 Debian Linux 系统上安装 PostgreSQL 数据库。
$ sudo apt-get install postgresql
此命令将安装 PostgreSQL 服务器和相关软件包。
$ /etc/init.d/postgresql status
我们使用postgresql status命令检查数据库的状态。
$ sudo -u postgres psql postgrespsql (9.5.10)Type "help" for help.postgres=# \password postgresEnter new password: Enter it again:
安装后,将使用空的默认密码创建一个具有管理权限的postgres用户。 第一步,我们需要为postgres设置密码。
$ sudo -u postgres createuser --interactive --password user12Shall the new role be a superuser? (y/n) nShall the new role be allowed to create databases? (y/n) yShall the new role be allowed to create more new roles? (y/n) nPassword:
我们创建一个新的数据库用户。
$ sudo -u postgres createdb testdb -O user12
我们使用createdb命令创建一个新的testdb数据库,该数据库将由user12拥有。
$ sudo vi /etc/postgresql/9.5/main/pg_hba.conf
我们编辑pg_hba.conf文件。
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections onlylocal all all trust# IPv4 local connections:host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust
为了能够在本地 PostgreSQL 安装中运行 Spring Boot 应用,我们将 Unix 域套接字和本地连接的身份验证方法更改为trust。
$ sudo service postgresql restart
我们重新启动 PostgreSQL 以启用更改。
$ psql -U user12 -d testdb -WPassword for user user12: psql (9.5.10)Type "help" for help.testdb=>
现在我们可以使用psql工具连接到数据库。
Spring Boot PostgreSQL 示例
以下应用是一个简单的 Spring Boot Web 应用,它使用 PostgreSQL 数据库。 我们有一个主页,带有一个链接,用于显示数据库表中的数据。 我们使用 Thymeleaf 模板系统将数据与 HTML 连接。
pom.xmlsrc├───main│ ├───java│ │ └───com│ │ └───zetcode│ │ │ Application.java│ │ ├───controller│ │ │ MyController.java│ │ ├───model│ │ │ City.java│ │ ├───repository│ │ │ CityRepository.java│ │ └───service│ │ CityService.java│ │ ICityService.java│ └───resources│ │ application.properties│ │ data-postgres.sql│ │ schema-postgres.sql│ ├───static│ │ index.html│ └───templates│ showCities.html└───test └───java
这是项目结构。
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.zetcode</groupId> <artifactId>springbootpostgreex</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.7.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.postgresql</groupId> <artifactId>postgresql</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build></project>
Spring Boot 启动器是一组方便的依赖项描述符,可以极大地简化 Maven 配置。 spring-boot-starter-parent具有 Spring Boot 应用的一些常用配置。 spring-boot-starter-web是使用 Spring MVC 构建 Web(包括 RESTful)应用的入门工具。 它使用 Tomcat 作为默认的嵌入式容器。 spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf是使用 Thymeleaf 视图构建 MVC Web 应用的入门工具。 spring-boot-starter-data-jpa是将 Spring Data JPA 与 Hibernate 结合使用的入门工具。
postgresql依赖项适用于 PostgreSQL 数据库驱动程序。
在spring-boot-maven-plugin提供了 Maven 的春季启动支持,使我们能够打包可执行的 JAR 或 WAR 档案。 它的spring-boot:run目标运行春季启动应用。
resources/application.properties
spring.main.banner-mode=offlogging.level.org.springframework=ERRORspring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=nonespring.datasource.initialization-mode=alwaysspring.datasource.platform=postgresspring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/testdbspring.datasource.username=postgresspring.datasource.password=s$cretspring.jpa.properties.hibernate.jdbc.lob.non_contextual_creation=true
在application.properties文件中,我们编写了 Spring Boot 应用的各种配置设置。
使用spring.main.banner-mode属性,我们可以关闭 Spring 标语。 要加载未嵌入的数据库,在 Spring Boot 2 中,我们需要添加spring.datasource.initialization-mode=always。 为避免冲突,我们使用spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none关闭自动模式创建。
在 spring 数据源属性中,我们设置了 PostgreSQL 数据源。
设置spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.jdbc.lob.non_contextual_creation选项可以避免最近发生的问题。 没有此选项,我们将收到以下错误:
java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException: Method org.postgresql.jdbc.PgConnection.createClob() is not yet implemented.
com/zetcode/model/City.java
package com.zetcode.model;import java.util.Objects;import javax.persistence.Entity;import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;import javax.persistence.GenerationType;import javax.persistence.Id;import javax.persistence.Table;@Entity@Table(name = "cities")public class City { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; private String name; private int population; public City() { } public City(Long id, String name, int population) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.population = population; } public Long getId() { return id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getPopulation() { return population; } public void setPopulation(int population) { this.population = population; } @Override public int hashCode() { int hash = 7; hash = 79 * hash + Objects.hashCode(this.id); hash = 79 * hash + Objects.hashCode(this.name); hash = 79 * hash + this.population; return hash; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } if (obj == null) { return false; } if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) { return false; } final City other = (City) obj; if (this.population != other.population) { return false; } if (!Objects.equals(this.name, other.name)) { return false; } return Objects.equals(this.id, other.id); } @Override public String toString() { final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("City{"); sb.append("id=").append(id); sb.append(", name='").append(name).append('\''); sb.append(", population=").append(population); sb.append('}'); return sb.toString(); }}这是City实体。 每个实体必须至少定义两个注解:@Entity和@Id。
@Entity@Table(name = "cities")public class City {@Entity注解指定该类是一个实体,并映射到数据库表。 @Table注解指定要用于映射的数据库表的名称。
@Id@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)private Long id;
@Id注解指定实体的主键,@GeneratedValue提供规范主键值的生成策略。
resources/schema-postgres.sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cities;CREATE TABLE cities(id serial PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255), population integer);
启动应用后,如果关闭了自动模式创建,则将执行schema-postgres.sql脚本。 该脚本将创建一个新的数据库表。
resources/data-postgres.sql
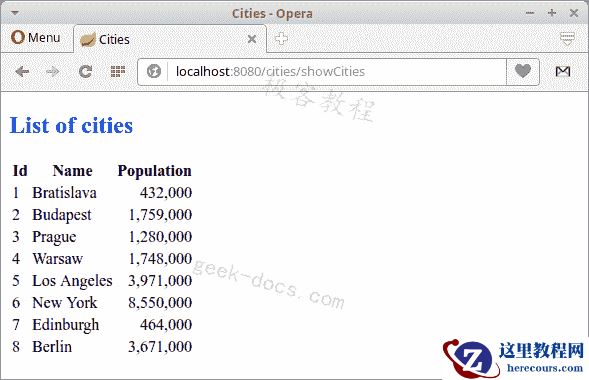
INSERT INTO cities(name, population) VALUES('Bratislava', 432000);INSERT INTO cities(name, population) VALUES('Budapest', 1759000);INSERT INTO cities(name, population) VALUES('Prague', 1280000);INSERT INTO cities(name, population) VALUES('Warsaw', 1748000);INSERT INTO cities(name, population) VALUES('Los Angeles', 3971000);INSERT INTO cities(name, population) VALUES('New York', 8550000);INSERT INTO cities(name, population) VALUES('Edinburgh', 464000);INSERT INTO cities(name, population) VALUES('Berlin', 3671000);之后,执行data-postgres.sql文件以用数据填充表。
com/zetcode/repository/CityRepository.java
package com.zetcode.repository;import com.zetcode.model.City;import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repositorypublic interface CityRepository extends CrudRepository<City, Long> {}通过从 Spring CrudRepository扩展,我们将为我们的数据存储库实现一些方法,包括findAll()。 这样,我们节省了大量样板代码。
com/zetcode/service/ICityService.java
package com.zetcode.service;import com.zetcode.model.City;import java.util.List;public interface ICityService { List<City> findAll();}ICityService提供了一种从数据源获取所有城市的合同方法。
com/zetcode/service/CityService.java
package com.zetcode.service;import com.zetcode.model.City;import com.zetcode.repository.CityRepository;import java.util.List;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class CityService implements ICityService { @Autowired private CityRepository repository; @Override public List<City> findAll() { var cities = (List<City>) repository.findAll(); return cities; }}CityService包含findAll()方法的实现。 我们使用存储库从数据库检索数据。
@Autowiredprivate CityRepository repository;
注入CityRepository。
var cities = (List<City>) repository.findAll();
存储库的findAll()方法返回城市列表。
com/zetcode/MyController.java
package com.zetcode.controller;import com.zetcode.model.City;import com.zetcode.service.ICityService;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import java.util.List;@Controllerpublic class MyController { @Autowired private ICityService cityService; @GetMapping("/showCities") public String findCities(Model model) { var cities = (List<City>) cityService.findAll(); model.addAttribute("cities", cities); return "showCities"; }}MyController包含一个映射。
@Autowiredprivate ICityService cityService;
我们在countryService字段中插入ICityService。
@GetMapping("/showCities")public String findCities(Model model) { var cities = (List<City>) cityService.findAll(); model.addAttribute("cities", cities); return "showCities";}我们将带有showCities路径的请求映射到控制器的findCities()方法。 默认请求是 GET 请求。 该模型将获取城市列表,并将处理过程发送到showCities.html Thymeleaf 模板文件。
resources/templates/showCities.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>Cities</title> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> </head> <body> <h2>List of cities</h2> <table> <tr> <th>Id</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Population</th> </tr> <tr th:each="city : {cities}"> <td th:text="{city.id}">Id</td> <td th:text="{city.name}">Name</td> <td th:text="{city.population}">Population</td> </tr> </table> </body></html>
在showCities.html模板文件中,我们在 HTML 表中显示数据。
resources/static/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html> <head> <title>Home page</title> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> </head> <body> <a href="showCities">Show cities</a> </body></html>
index.html中有一个链接,显示所有城市。
com/zetcode/Application.java
package com.zetcode;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplicationpublic class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); }}Application设置 Spring Boot 应用。 @SpringBootApplication启用自动配置和组件扫描。
$ mvn spring-boot:run
应用运行后,我们可以导航到localhost:8080。
在本教程中,我们展示了如何在 Spring Boot 应用中使用 PostgreSQL 数据库。