C++程序 针对由链表表示的两个数进行加法的-2
给定两个由链表表示的数字,编写一个函数返回它们的和。和列表是两个输入数字的加法的链表表示。不允许修改链表。同时,不允许使用显示的额外空间(提示:使用递归)。
示例:
输入:
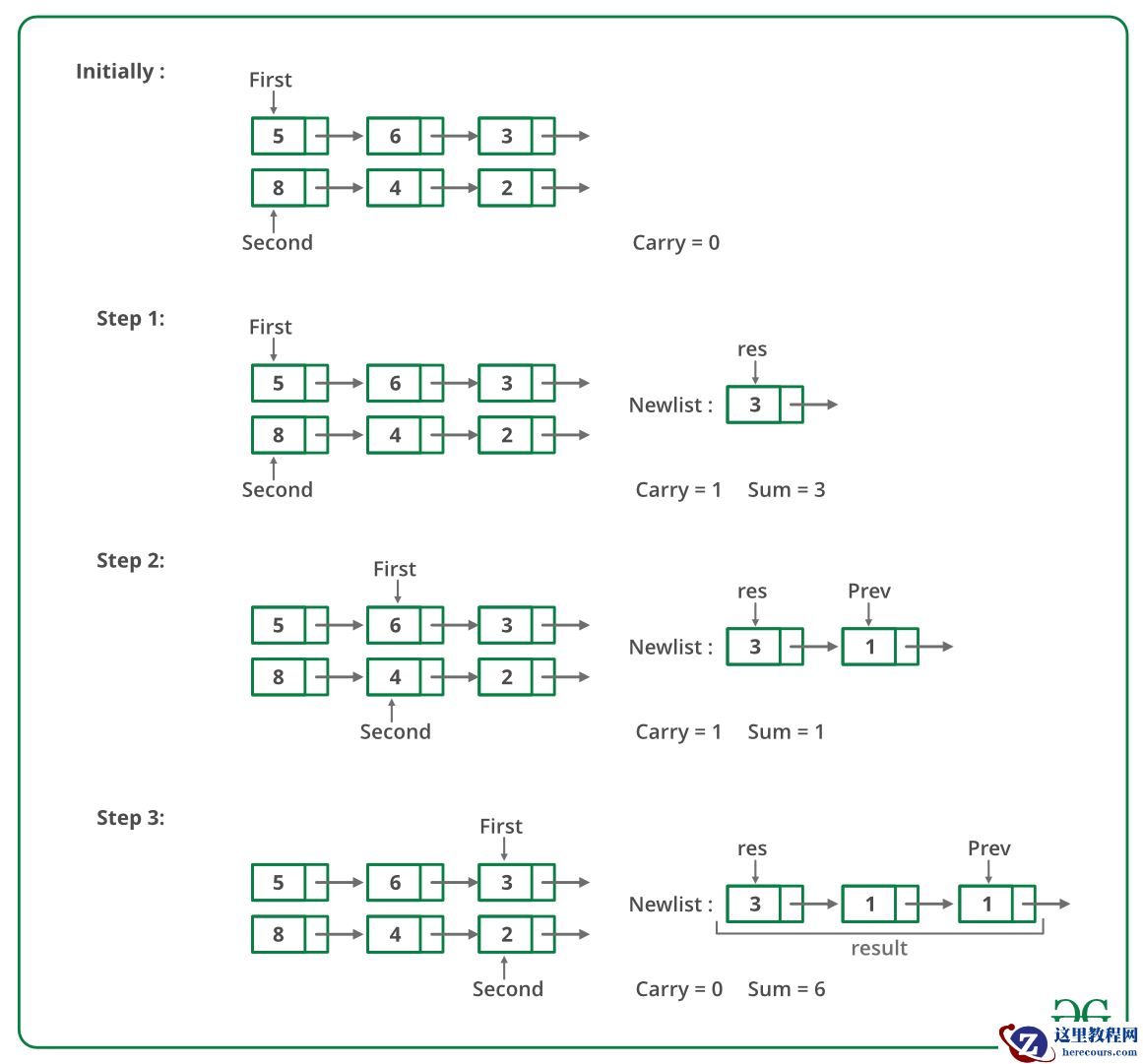
第一个列表:5-〉6-〉3
第二个列表:8-〉4-〉2
输出:
结果列表:1-〉4-〉0-〉5
实践
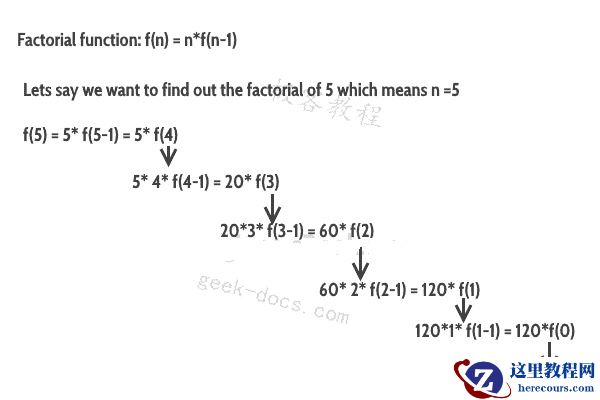
我们已经在此处讨论了一种针对链表的解决方案,其中最不重要的数字是列表的第一个节点,而最重要的数字是最后一个节点。在这个问题中,最重要的节点是第一个节点,而最不重要的数字是最后一个节点,我们不能修改这些列表。这里使用递归从右到左计算总和。
以下是步骤:
- 计算给定的两个链表的大小。如果大小相同,则使用递归计算总和。在递归调用堆栈中保持所有节点直到最右边的节点,计算最右边节点的总和并向左侧转发进位。如果大小不同,则按以下步骤进行操作:
下面是上述方法的演示运行:
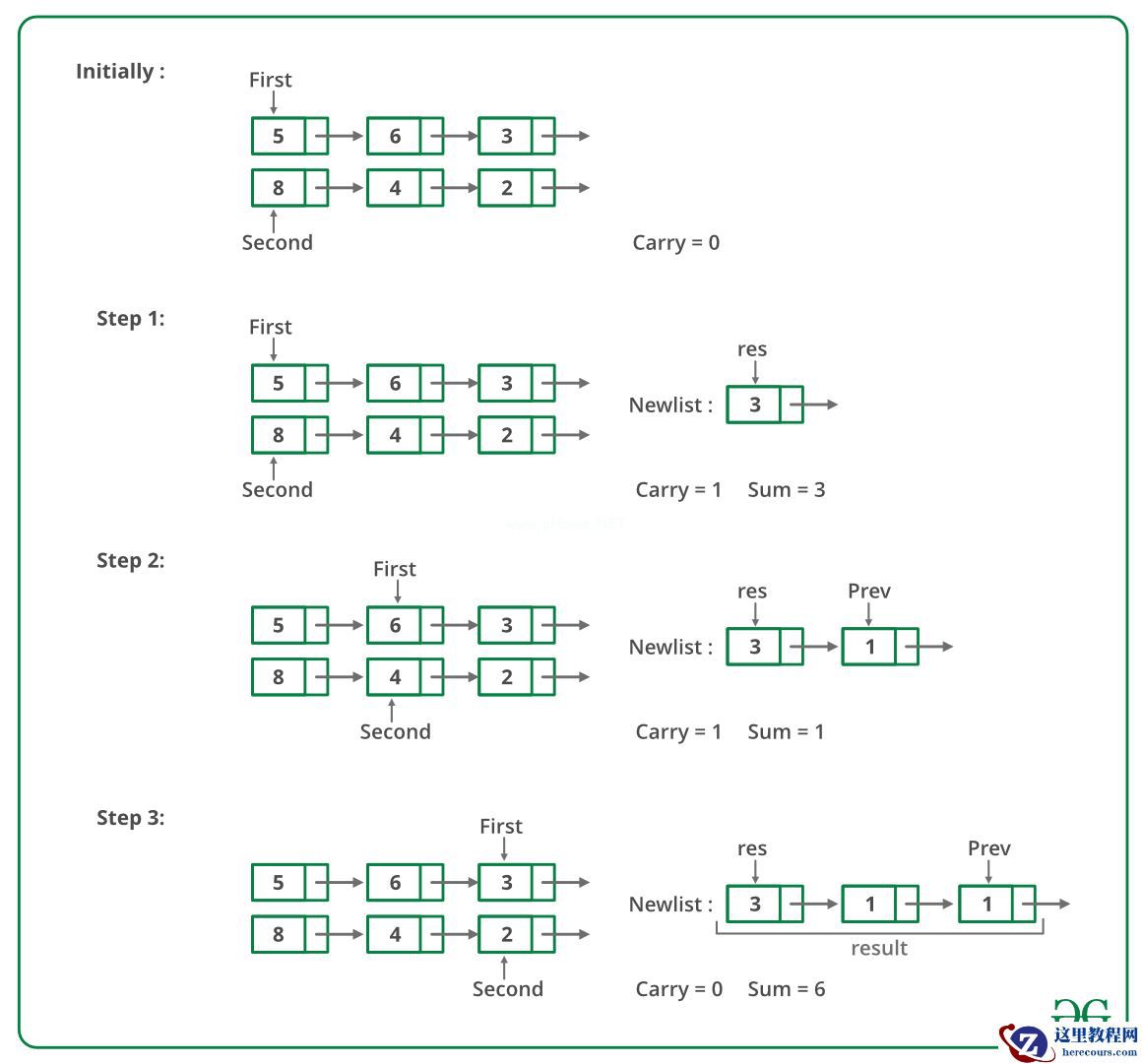
下面的图像实现了上述方法。
// C++递归程序,用于将两个链接列表相加#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// 链接列表节点class Node{ public: int data; Node* next;};typedef Node node;/* 将节点插入到链接列表的开头 */void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data){ // 分配节点 Node* new_node = new Node[(sizeof(Node))]; // 写入数据 new_node->data = new_data; // 将旧的列表与新的节点链接 new_node->next = (*head_ref); // 将头移到新节点 (*head_ref) = new_node;}// 遍历和打印链接列表void printList(Node* node){ while (node != NULL) { cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next; } cout << endl;}// 交换两个节点指针的函数void swapPointer(Node** a, Node** b){ node* t = *a; *a = *b; *b = t;}/* 计算链接列表的大小 */int getSize(Node* node){ int size = 0; while (node != NULL) { node = node->next; size++; } return size;}// 将相同大小的两个链接列表相加,分别由head1和head2表示,并返回结果的头部链接列表。当从递归返回时,进位被传播node* addSameSize(Node* head1, Node* head2, int* carry){ // 由于该函数假设链接列表的大小相同,因此检查任意两个头指针之一 if (head1 == NULL) return NULL; int sum; // 分配内存给当前两个节点之和的节点 Node* result = new Node[(sizeof(Node))]; // 递归添加剩下的节点并取得进位 result->next = addSameSize(head1->next, head2->next, carry); // 把当前两个数字和进位相加 sum = head1->data + head2->data + *carry; *carry = sum / 10; sum = sum % 10; // 分配和给结果列表的当前节点 result->data = sum; return result;}// 在较小的列表被添加到相同大小的大列表的子列表之后调用此函数。一旦右子列表被添加,就必须将进位加到较大列表的左边,以得到最终结果。void addCarryToRemaining(Node* head1, Node* cur, int* carry, Node** result){ int sum; // 如果未遍历相同数量的节点,则加法进位 if (head1 != cur) { addCarryToRemaining(head1->next, cur, carry, result); sum = head1->data + *carry; *carry = sum / 10; sum %= 10; // 把这个节点添加到结果的最前面 push(result, sum); }}// 添加由head1和head2表示的两个链接列表。两个列表的和存储在由result引用的列表中void addList(Node* head1, Node* head2, Node** result){ Node* cur; // 第一个列表是空的 if (head1 == NULL) { *result =head2; return; } // 第二个列表是空的 else if (head2 == NULL) { *result = head1; return; } int size1 = getSize(head1); int size2 = getSize(head2); int carry = 0; // 如果大小相等,则将相同大小的列表相加 if (size1 == size2) *result = addSameSize(head1, head2, &carry); else { int diff = abs(size1 - size2); // 第一个列表应始终大于第二个列表。如果不是,则交换指针 if (size1 < size2) swapPointer(&head1, &head2); // 遍历大的列表,这个遍历从两个列表的剩余部分开始 for (cur = head1; diff--; cur = cur->next); // 现在对于两个相同大小的列表,使用函数addSameSize()来做加法 *result = addSameSize(cur, head2, &carry); // 使用现有大列表的引用,加上进位数字 addCarryToRemaining(head1, cur, &carry, result); } // 如果有进位,则将它附加到结果的第一个元素 if (carry) push(result, carry);}// 主函数int main(){ Node *head1 = NULL, *head2 = NULL, *result = NULL; int arr1[] = {9, 9, 9}; int arr2[] = {1, 8}; int size1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]); int size2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]); // 创建第一个链表 int i; for (i = size1 - 1; i >= 0; --i) push(&head1, arr1[i]); // 创建第二个链表 for (i = size2 - 1; i >= 0; --i) push(&head2, arr2[i]); // 添加两个列表,并要求输出结果列表 addList(head1, head2, &result); printList(result); return 0;}输出:
1 0 1 7
时间复杂度:
O(m+n),其中m和n是给定两个链表的大小。
辅助空间 :递归调用栈占用O(m+n)的空间
迭代方法:
此实现没有任何递归调用开销,因此是迭代解决方案。
由于我们需要从两个链表的最后开始添加数字,因此这里我们将使用栈数据结构来实现它。
我们将首先从给定的两个链表中创建两个栈。然后,我们将循环运行直到两个栈都为空。在每次迭代中,我们跟踪进位。最后,如果carry>0,那么这意味着我们需要在结果列表的开头额外的节点来容纳该进位。// C++迭代程序添加两个// 链接列表 # include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std; // 链接列表节点 class Node { public: int data; Node* next; }; // 将新节点推入// 链接列表void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data) { // 分配节点 Node* new_node = new Node[(sizeof(Node))]; // 放入数据 new_node->data = new_data; // 将旧列表链接到 // 新节点 new_node->next = (*head_ref); // 将头移动到指向 // 新节点 (*head_ref) = new_node; } // 添加两个新数字Node* addTwoNumList(Node* l1, Node* l2){ stack<int> s1,s2; while(l1 != NULL) { s1.push(l1->data); l1 = l1->next; } while(l2 != NULL) { s2.push(l2->data); l2 = l2->next; } int carry = 0; Node* result = NULL; while(s1.empty() == false || s2.empty() == false) { int a = 0,b = 0; if(s1.empty() == false) { a = s1.top(); s1.pop(); } if(s2.empty() == false) { b = s2.top(); s2.pop(); } int total = a + b + carry; Node* temp = new Node(); temp->data = total % 10; carry = total / 10; if(result == NULL) { result = temp; } else { temp->next = result; result = temp; } } if(carry != 0) { Node* temp = new Node(); temp->data = carry; temp->next = result; result = temp; } return result;} // 打印链接列表void printList(Node *node) { while (node != NULL) { cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next; } cout < endl; } // 驱动程序int main() { Node *head1 = NULL, *head2 = NULL; int arr1[] = {5, 6, 7}; int arr2[] = {1, 8}; int size1 = (sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0])); int size2 = (sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0])); // 创建第一个列表为5->6->7 int i; for (i = size1-1; i >= 0; --i) push(&head1, arr1[i]); // 将第二个列表创建为1->8 for (i = size2-1; i >= 0; --i) push(&head2, arr2[i]); Node* result = addTwoNumList(head1, head2); printList(result); return 0; } 输出:
5 8 5
时间复杂度: O(m + n),其中m和n是给定两个链表中节点的数量。
辅助空间: O(n),其中n是栈中元素的数量