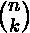Guava – Multiset接口
Multiset接口简介: Multiset是一个支持顺序无关的平等的集合,像Set一样,但可能有重复的元素。我们可能认为多集就是一个列表,但事实并非如此。
Lists可以容纳同一对象的重复,而且Lists总是有序的。集合不能容纳重复的元素,而且集合接口也不能保证其顺序。所以,多数据集是介于列表和集合之间的一种灰色区域。允许重复,但不保证顺序。 Multiset有时也被称为包。在多集中,和集合一样,与图元相比,元素的顺序在多集中是不相关的。例如:多集{a,a,b}和{a,b,a}是相等的。
有两种主要的方式来看待多集:
这就像一个没有排序约束的 ArrayList < E > ,即排序并不重要。这就像一个 Map <E, Integer>,有元素和计数。Multiset接口要点:
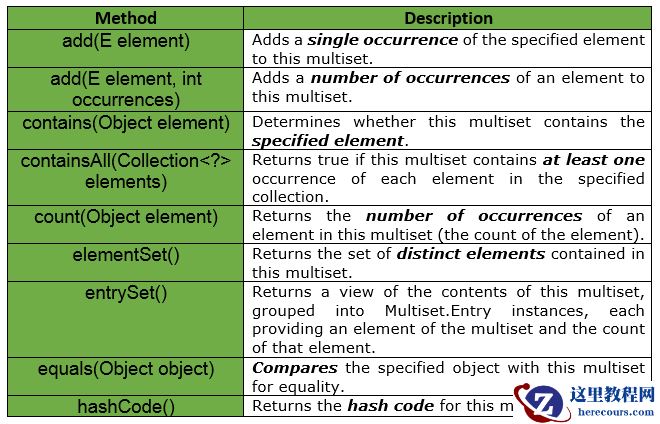
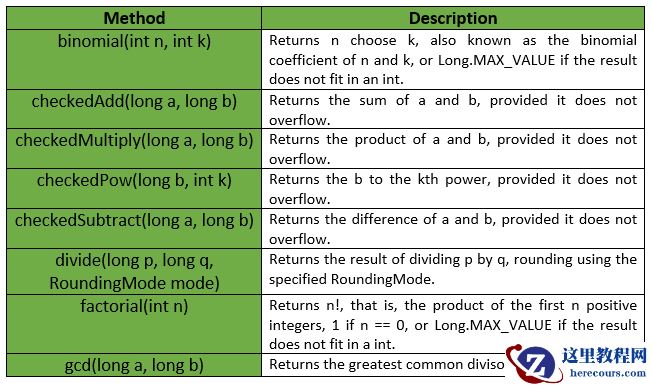
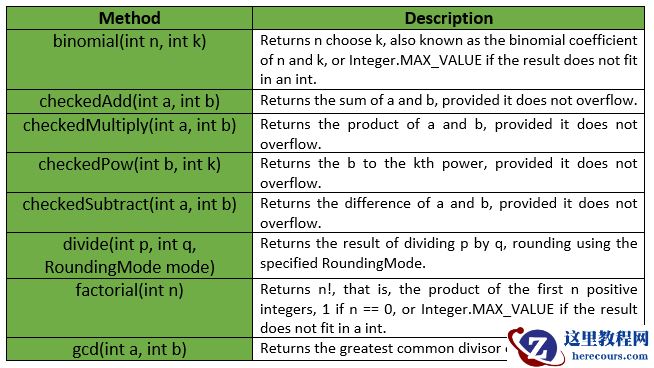
Multiset是一个集合,它支持与顺序无关的平等,就像Set一样,但可能有重复的元素。Multiset中彼此相等的元素被称为同一单一元素的出现。一个多集合中一个元素出现的总数被称为该元素的 count 。因为一个元素的计数是用int表示的,所以一个多数据集永远不会包含超过Integer.MAX_VALUE的任何一个元素的出现次数。Multiset使用Object.equals(java.lang.Object)来确定两个实例是否应被视为 “相同”,除非实现中另有规定。Multiset < E > ,只有具有正数的元素。任何元素都不能有负数,计数为0的值被认为不在多数据集中。它们不会出现在 elementSet() 或 entrySet() 视图中。multiset.size()返回集合的大小,它等于所有元素的计数之和。对于独立元素的数量,使用 elementSet().size()。例如,add(E)使multiset.size()增加1。multiset.iterator()对每个元素的每个出现进行迭代,所以迭代的长度等于multiset.size()。Multiset支持添加元素、删除元素或直接设置元素的计数。setCount(element, 0)等同于删除该元素的所有出现次数。multiset.count(element)对于不在multiset中的元素总是返回0。Multiset接口声明: com.google.common.collect.Multiset接口的声明如下。
@GwtCompatiblepublic interface Multiset extends Collection
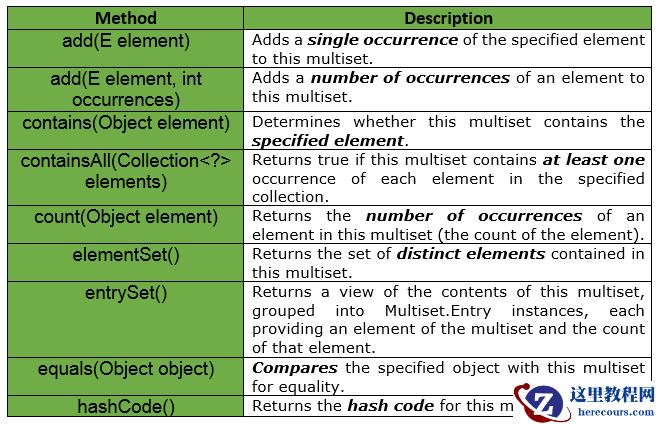
Example : 我们知道,如果两个相等的元素被添加到java.util.Set中,那么第二个元素将被丢弃。
// Java implementation to show if 2// equal elements are added to// java.util.Set, then the 2nd element// will be discarded import java.util.Set;import java.util.HashSet; // Set of StringsSet<String> set = new HashSet(); // Adding elements to the setset.add("Geeks");set.add("Geeks"); System.out.println(set); // The output will be [Geeks]但是,如果我们使用Guava的Multiset,那么重复的元素就不会被丢弃了。请看下面的代码实现:
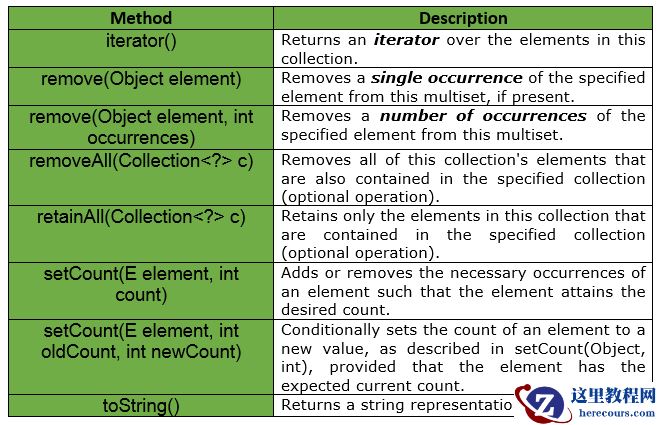
// Java implementation to show if 2// equal elements are added to// Multiset, then the 2nd element// will not be discarded import com.google.common.collect.HashMultiset;import com.google.common.collect.Multiset; // Multiset of StringMultiset<String> multiset = HashMultiset.create(); // Adding elements to the setmultiset.add("Geeks");multiset.add("Geeks"); System.out.println(multiset); // The output will be [Geeks X 2]下面给出的是Guava的Multiset接口所提供的一些其他方法。
实现 : Guava提供了许多Multiset的实现,这些实现与JDK map的实现大体一致。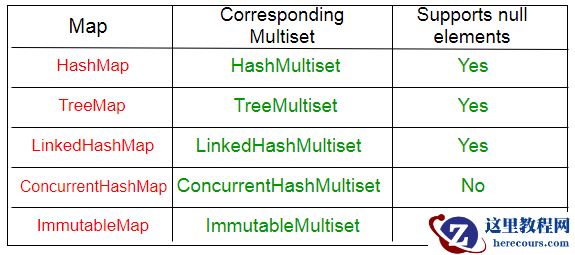
Set的例子 :
// Java code to show implementation// of a Setimport java.util.*; import com.google.common.collect.HashMultiset;import com.google.common.collect.Multiset; class GuavaTester { // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { // Creating a Set of Strings Set<String> set = new HashSet(); // Adding elements to set set.add("Geeks"); set.add("for"); set.add("Geeks"); set.add("for"); set.add("GeeksforGeeks"); set.add("Geeks"); set.add("GeeksforGeeks"); set.add("Geeks"); // printing the total size of the set System.out.println("Total Size is : " + set.size()); // print the occurrence of each element System.out.println("Occurrences of Geeks are : " + Collections.frequency(set, "Geeks")); System.out.println("Occurrences of for are : " + Collections.frequency(set, "for")); System.out.println("Occurrences of GeeksforGeeks are : " + Collections.frequency(set, "GeeksforGeeks")); }}输出:
Total Size is : 3Occurrences of Geeks are : 1Occurrences of for are : 1Occurrences of GeeksforGeeks are : 1
Multiset的例子 :
// Java code to show implementation// of a Multisetimport java.util.*; import com.google.common.collect.HashMultiset;import com.google.common.collect.Multiset; class GuavaTester { // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { // Creating a Multiset of Strings Multiset<String> multiset = HashMultiset.create(); // Adding elements to multiset multiset.add("Geeks"); multiset.add("for"); multiset.add("Geeks"); multiset.add("for"); multiset.add("GeeksforGeeks"); multiset.add("Geeks"); multiset.add("GeeksforGeeks"); multiset.add("Geeks"); // printing the total size of the multiset System.out.println("Total Size is : " + multiset.size()); // print the occurrence of each element System.out.println("Occurrences of Geeks are : " + multiset.count("Geeks")); System.out.println("Occurrences of for are : " + multiset.count("for")); System.out.println("Occurrences of GeeksforGeeks are : " + multiset.count("GeeksforGeeks")); }}输出:
Total Size is : 8Occurrences of Geeks are : 4Occurrences of for are : 2Occurrences of GeeksforGeeks are : 2